Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This may influence which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations.
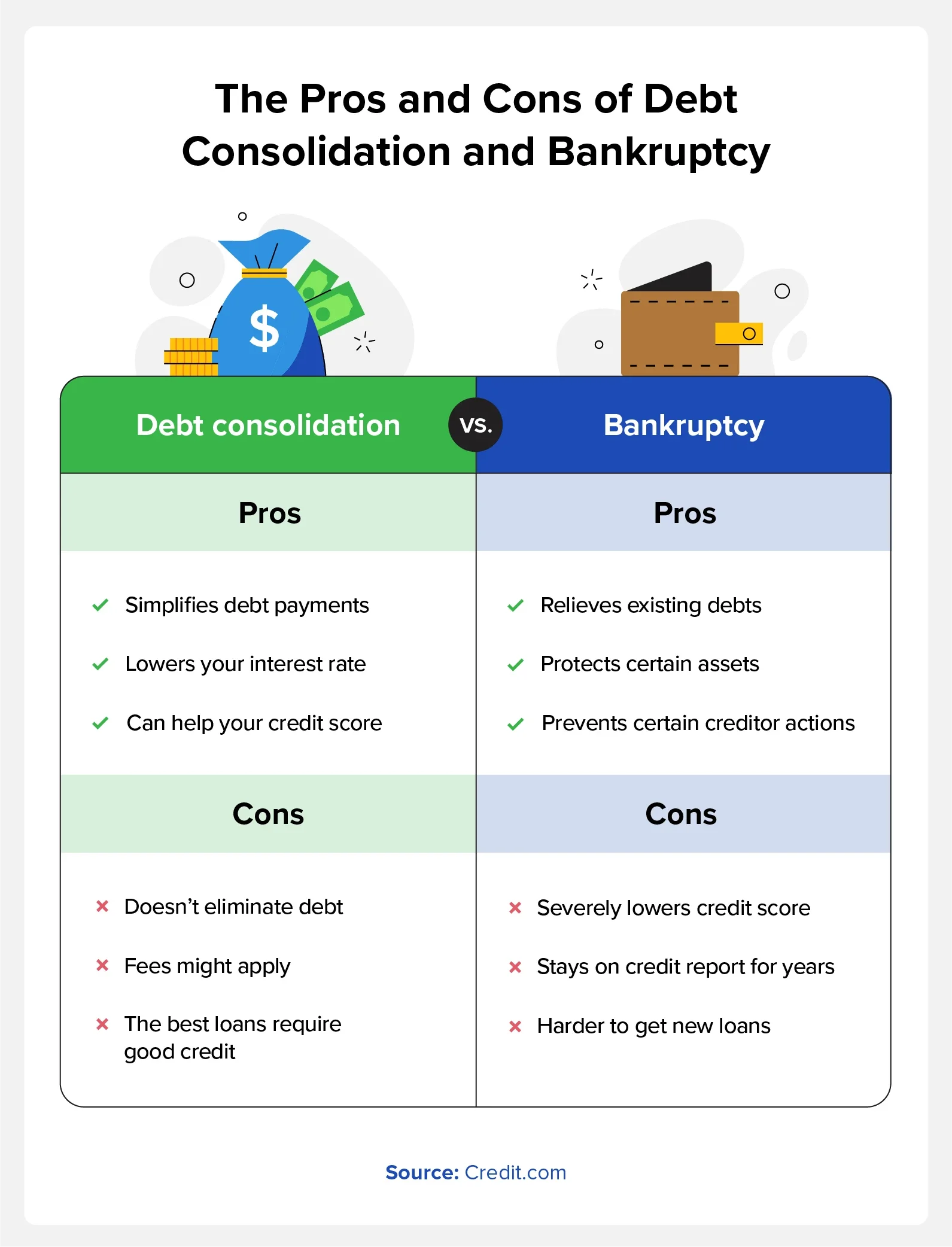
Debt consolidation combines multiple debts into one and can help your credit score. Bankruptcy can reduce your total debt at the cost of ruining your credit.
Debt consolidation and bankruptcy are two options for debt relief that have distinct advantages and drawbacks.
- Debt consolidation means merging multiple existing debts into a single new loan. Debt consolidation loans won’t clear your current debt, but they can help you minimize late payments and other fees incurred from having multiple loans.
- Bankruptcy involves discharging or restructuring all your debts—but it stays on your credit report for many years, depending on which chapter you file for. It’s generally considered a last resort when no other debt-relief options are appropriate for your situation.
Which debt relief option is right for you depends on your financial situation. Below, we’ll compare debt consolidation vs. bankruptcy and discuss some things to consider when choosing a debt relief service.
What Is Debt Consolidation?
Debt consolidation involves merging multiple debts into one loan. The goal here is to streamline the process of paying down your total balance while also improving your credit utilization rate.
Debt consolidation loans and balance transfer credit cards are crucial to this process. That means you need to be able to qualify for new credit, which can be difficult if you regularly make late payments or have collection accounts on your credit report.
When you consolidate, your new debt won’t be in collections, and your previous debts can show up as “paid in full” on your credit report. One of our tips for improving your credit history is to consistently make payments on new accounts. Adopting this habit will help you improve your credit over time.
Is Debt Consolidation a Good Idea?
Debt consolidation can be an excellent tool for people who would rather pay down one loan instead of managing multiple debts. Consolidation is also a good idea for people with good or better credit scores, as better credit can help you secure the best loan terms.
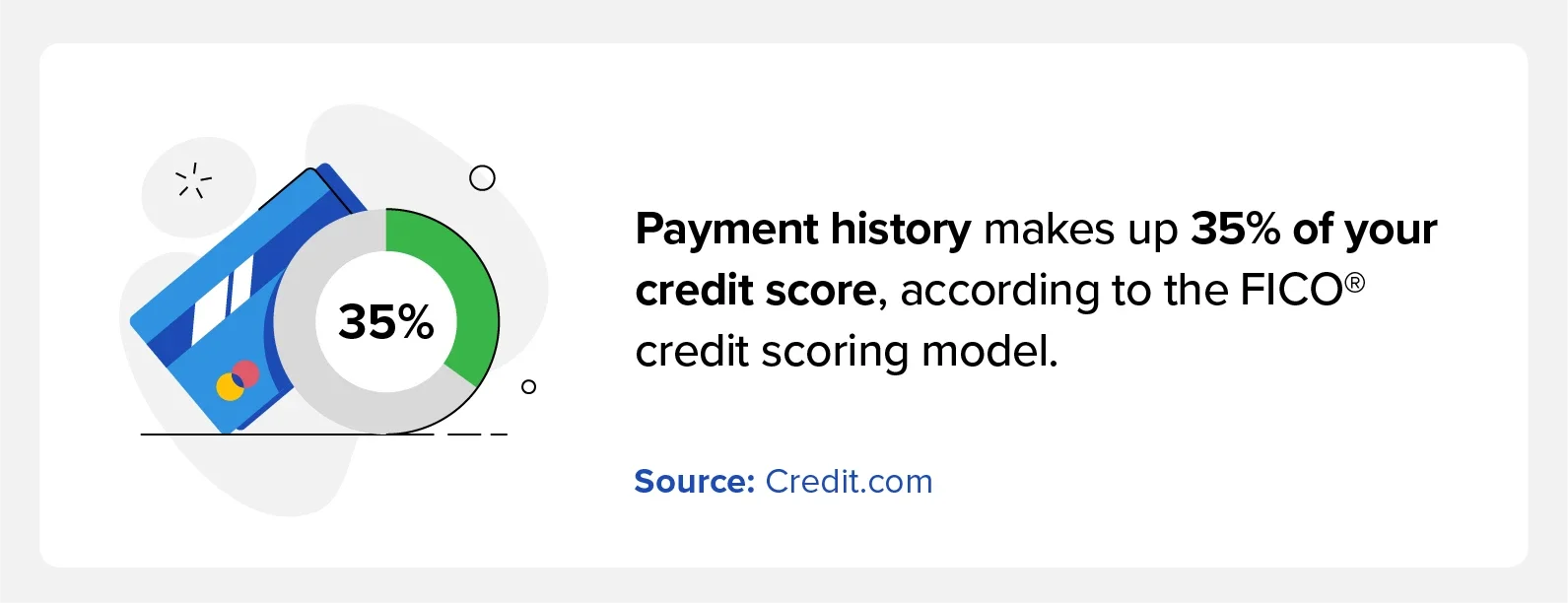
Payment history makes up 35% of your credit score, according to the FICO® credit scoring model. Knowing how your credit score is calculated and consistently paying off your minimum balance each month are vital to credit score growth.
What Is Bankruptcy?
Bankruptcy is a legal restructuring of your debts. When you file for bankruptcy, the court considers your debts and your income. Depending on the type of bankruptcy you file, you may need to submit a plan for paying back some of your debts. However, the result of finalizing the bankruptcy process is that most or all of the debts you entered with are considered discharged.
Whether you file Chapter 7, 13, or 11, if your bankruptcy is successful, you can start with a “clean slate” as far as what you owe goes. However, your credit score after bankruptcy procedures are finished will be drastically low. Your credit report will still reflect the late payments and issues leading up to the bankruptcy. The bankruptcy itself will also stay on your credit report for seven to 10 years, depending on the type of bankruptcy you file.
When Should I File for Bankruptcy?
As mentioned previously, bankruptcy should usually be your last resort. If you’re unable to secure a reasonable consolidation loan or if you don’t possess the funds needed to pay off your debts, bankruptcy might be worth considering.
It’s worth noting that filing for bankruptcy will affect people with higher credit more than individuals with lower credit. We also strongly recommend learning how to rebuild your credit after bankruptcy long before you file. Taking swift action can lessen the severity of filing for bankruptcy.
What Are Balance Transfer Cards?
For those wondering, “how do debt relief options affect your credit score?” it’s crucial to understand the other options you might have. If you’re primarily dealing with high-interest credit card debt and you feel like you’ll never get ahead on it, you could consider a balance transfer card.
The best balance transfer cards typically come with low introductory APR offers. You can transfer existing balances to the new card and not pay interest on it for a certain amount of time. That lets you make payments on the balance and pay it off faster. One of the most common is closing your older accounts. We recommend keeping your old accounts open and just using them less.
Maintain Strong Credit With Credit.com
If you’re not dealing with credit card debt or don’t want to open another credit card account, then you might consider a debt consolidation loan. These loans let you convert your debt to a single loan, which makes managing your financial life that much easier.
Whatever debt relief option you choose, Credit.com has your back. Sign up for our to keep track of your finances and additional tips and tricks for improving your financial health.
No matter how you plan to increase your revenue, maintaining strong credit is pivotal. Good or even excellent credit scores can help you secure lucrative loans and might even open the door to higher-paying positions. With Credit.com’s ExtraCredit service, you’ll get reliable updates about your credit score and tailor-made strategies to help you increase your standing.
You Might Also Like
May 30, 2023
Managing Debt
September 7, 2021
Managing Debt
December 23, 2020
Managing Debt





